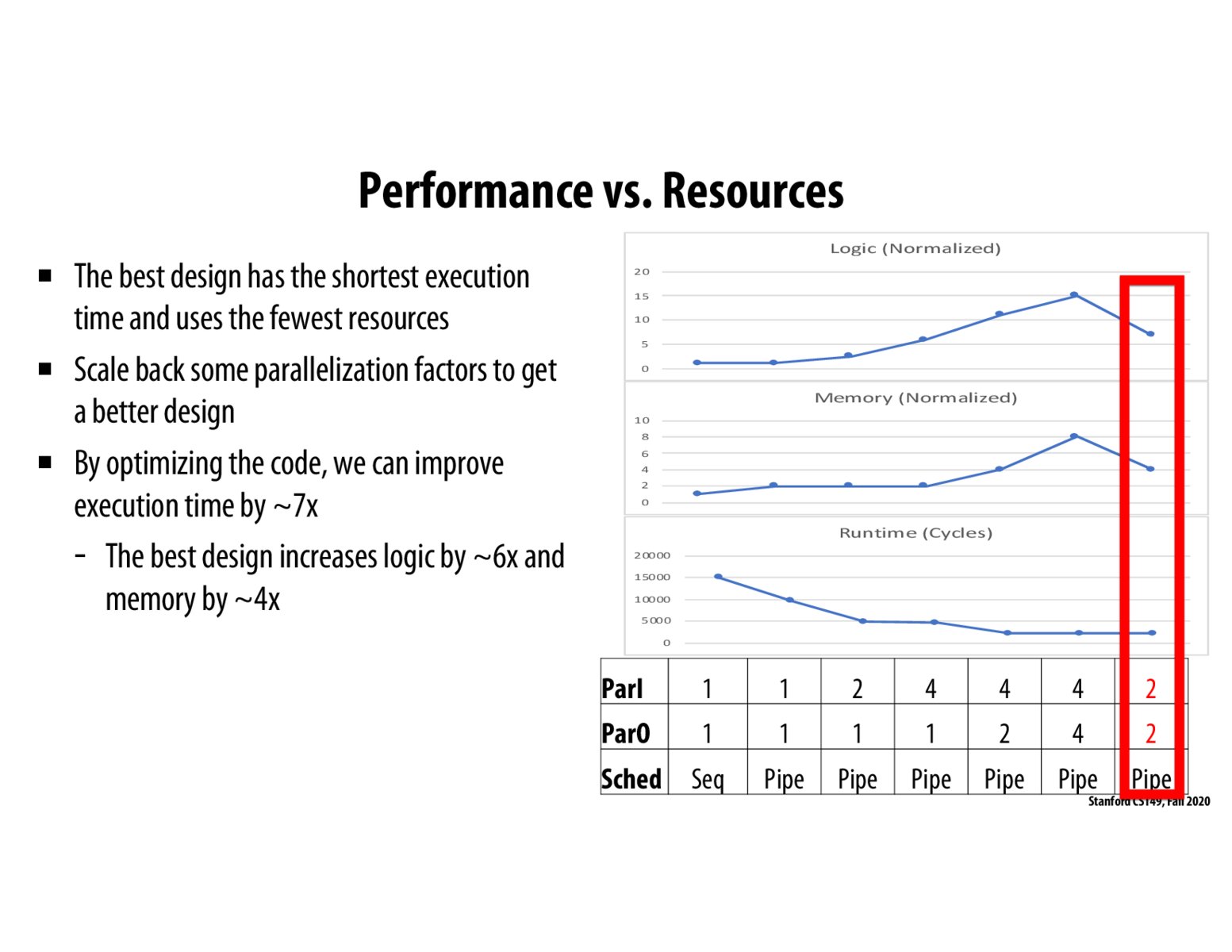


Key principle here for choosing 2,2 parallelization here (as opposed to 4,4 in the second-to-last column) is because we want to optimize the tradeoffs between performance and amount of resources used. Using a 4,4 parallelization, as shown on previous slides, gives us a slightly higher performance, but we use 2x as much memory and compute resources on hardware, which is wasteful. Thus, once we've reached bottlenecks (here the bottlenecks are memory bandwidth and longest inner controller time), where increased parallelization no longer leads to leaps of performance gains, it's often worth scaling back to save on resources.

A great resource for reading up about performance measurements is MLPerf. The website explains the different "fair" metrics for comparing implementations against a standard set of tests. MLPerf
Please log in to leave a comment.
Most of this performance optimization process is manual and the stats provided by Spatial would assist programmers in achieving better optimizations.