Back to Lecture Thumbnails

Claire

yonkus
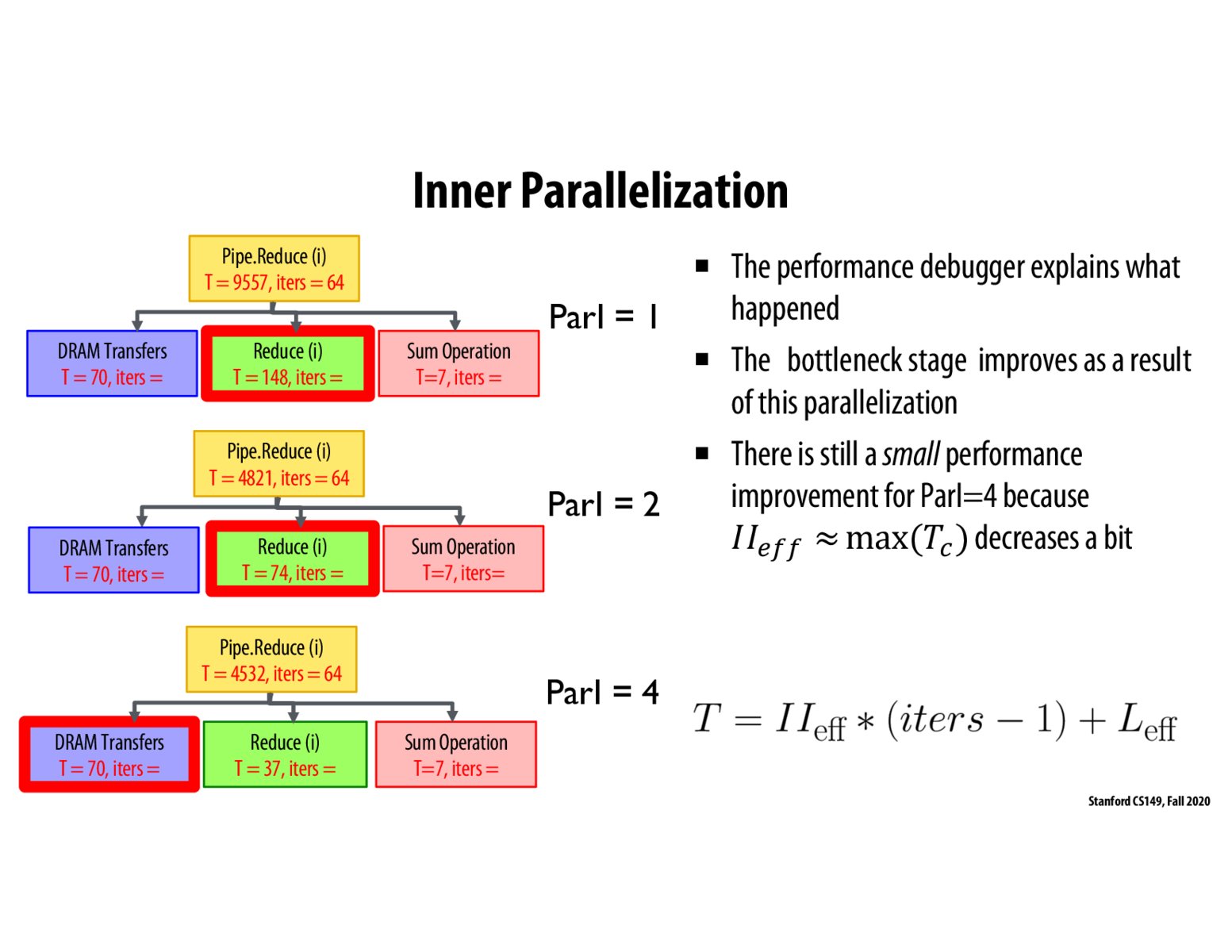
If the sum operation had a greater number for T, would that in turn become the bottleneck? It seems like the inner parallelization only affects the reduce function, is there a way to parallelize the summation as well?

haiyuem
@yonkus I think what you said should be addressed when parallelizing the outer loop

cbfariasc
Effectively, increasing the performance of the bottleneck is the only way to increase the performance of the entire parallel pipeline, since the performance overall is measured by the bottleneck.
Please log in to leave a comment.
Copyright 2020 Stanford University
As seen in the picture above, when going from 2 to 4, we are able to cut the Reduce(i) cycles in half, but we will see no significant speedup since the bottleneck will shift from Reduce(i) to DRAM Transfers since it has T=70 which is greater than Reduce(i)'s T=37.