

It seemed like the key difference that allowed Halide (and really any DSL) to be productive rather than general is that it provides a high-level interface akin to those seen in general-purpose high-level languages, but rather than providing a high-level interface that can handle various operations with a relatively small number of details it provides a high-level interface that will handle very specific operations with a large number of key details. So, it is effectively condensing complex but frequently seen pieces of code (such as the raw C++ blur code) into a single call for the programmer (as do general languages), but then proceeding to ask the programmer for non-trivial pieces of information about how the underlying C++ WOULD BE written. In doing so it makes the code much less general (imagine a generic .blur() function in python) but also greatly decreases workload for the programmer.

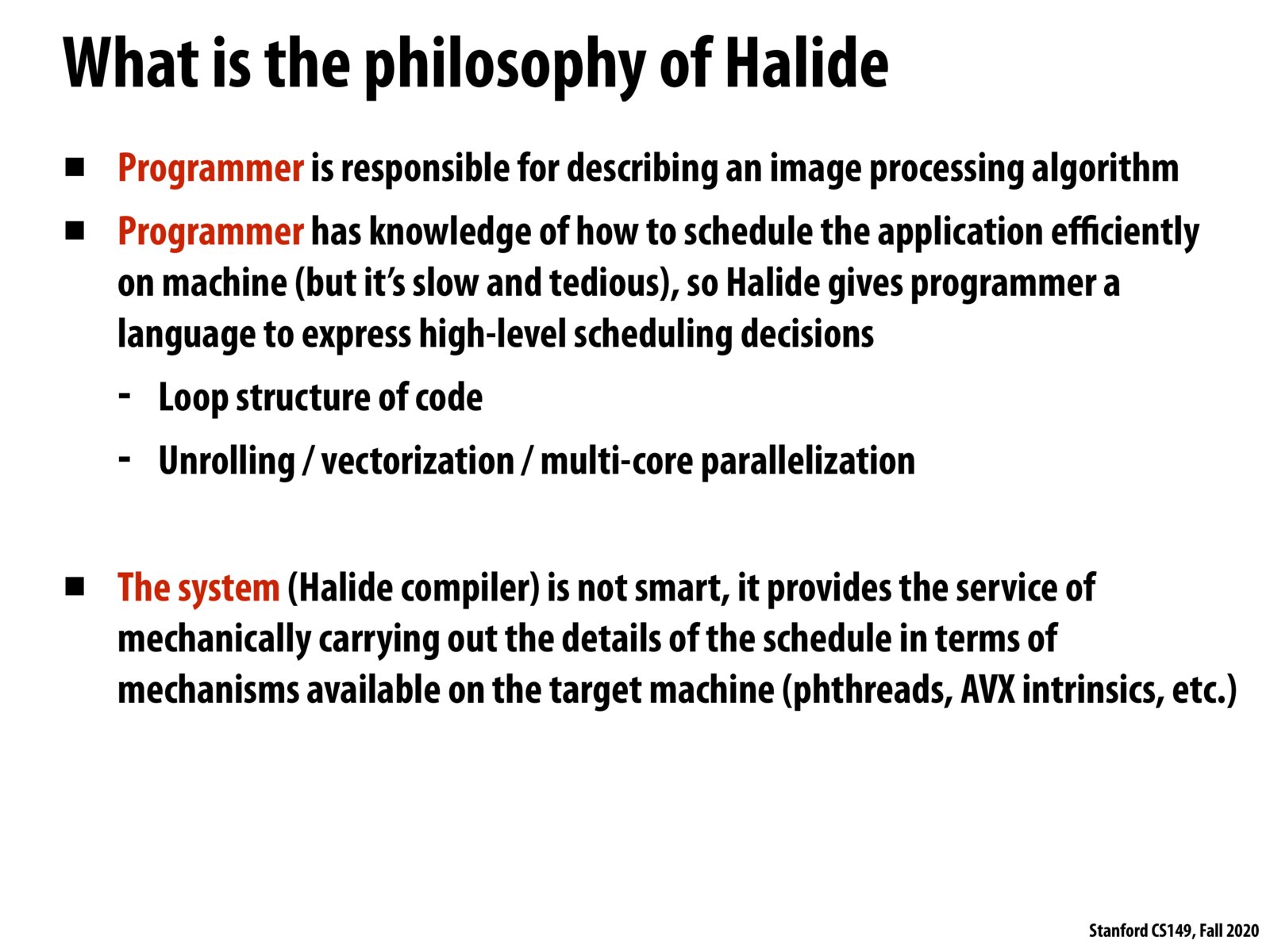
I thought that Halide had been developed enough to automatically generate more efficient scheduling implementations than most programmers can design, would that not include the loop structure, unrolling, vectorization, and multi-core parallelization?

@cbfariasc Halide is responsible for taking your high level description of how to schedule and generate instructions for specific architecture - that's the catch. So the programmer still needs to provide a high level description of the loop structure.

My understanding of Halide is that it contains very efficient implementation for commonly used algorithms in computer graphs but also allows users to specify the scheduling. Therefore, users with deep knowledge about their machines can leverage the computing resources to the largest extent, but at the same time have efficient algorithms "for free".
Please log in to leave a comment.
I thought it was cool to learn about a language that allows us to write more high level parallelization and optimize the writing time of our programs so that we can iterate and test our programs much faster than what we did for assignment 3 (lol). What are specific types of graphics programs that benefit more from Halide-like optimization than say like CUDA optimization (not sure if I missed this in lecture)?